Thinking about buying a home in 2024? With Canadian mortgage rates sitting between 6.39% and 7.34% for fixed options—and variable rates fluctuating from 6.45% to 6.90%—the stakes couldn’t be higher. As rates continue to shift, homebuyers are under more pressure than ever to choose the right mortgage type.
Selecting between a fixed or variable mortgage isn’t just a numbers game; it’s one of the biggest financial decisions you’ll make. Fixed-rate mortgages offer stability, while variable rates tempt with potential savings—but come with some uncertainty.
In this article, you’ll learn the pros and cons of each mortgage type, discover when each option makes the most sense, and get practical advice on finding the right fit for your homebuying journey.
Current Mortgage and Prime Rate Trends: What to Watch in 2024
Prime Rates Overview
Prime rates in Canada are critical benchmarks for determining variable mortgage rates. These rates are set by the country’s major financial institutions and are influenced by the Bank of Canada’s overnight lending rate.
As of October 23, 2024, the prime rate at most of Canada’s “Big Six” banks is 6.45%, with the exception of TD Bank, which has a slightly higher prime mortgage rate of 6.70%.
These rates are important for homebuyers considering variable-rate mortgages, as they directly impact monthly payments.
Mortgage Rates from Canada’s Big Banks
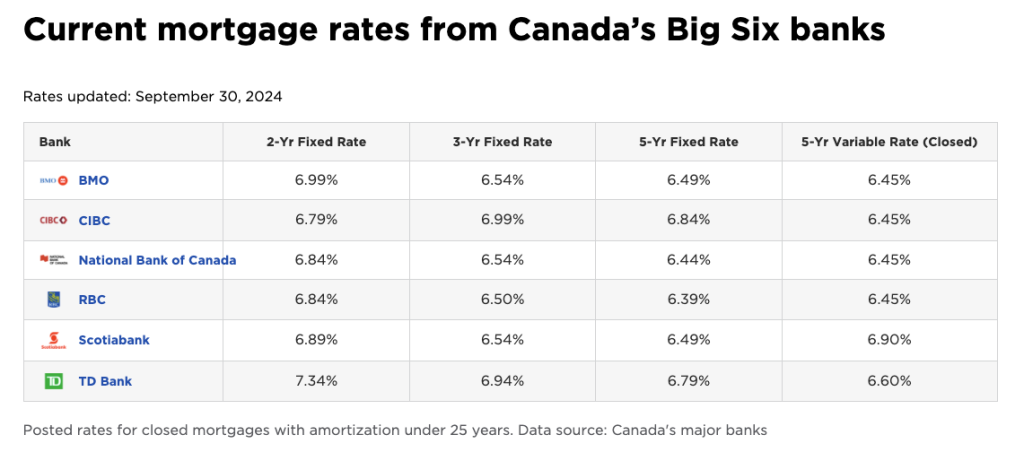
For homebuyers considering fixed-rate mortgages, here’s an overview of the current rates offered by Canada’s top banks:
- 2-Year Fixed Rate: Ranges from 6.79% to 7.34%
- 5-Year Fixed Rate: Ranges from 6.39% to 6.79%
- 5-Year Variable Rate: Generally around 6.45% to 6.90%
These rates vary depending on the term length and lender, but they provide a snapshot of the current market for those looking to lock in their mortgage rates or opt for a variable rate.
For personalized guidance, Cruz Financial Group is here to help you find the perfect mortgage fit for your needs.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage in Canada is a loan where the interest rate remains constant throughout the entire term of the mortgage, no matter how market conditions change. This means your monthly payments stay the same, offering predictability and stability, which can be especially comforting in fluctuating interest rate environments. This Canadian mortgage type is tied to bond yields, which means they tend to rise when bond prices fall and vice versa.
How It Works
With a fixed-rate mortgage in Canada, the interest rate is locked in from the start. Even if market rates rise, your mortgage rate—and your monthly payments—won’t change. This is particularly advantageous for borrowers looking to plan their long-term finances.
However, fixed-rate mortgages typically come with slightly higher initial rates compared to variable-rate mortgages, as lenders hedge against potential market increases in interest rates.
Pros
- Stable monthly payments: You know exactly what to expect, making budgeting easier.
- Long-term security: Ideal for buyers who plan to stay in their homes for several years.
- Protection from rising rates: If interest rates increase, your fixed rate won’t be affected.
- Easier financial planning: Since payments don’t fluctuate, it’s simpler to manage long-term expenses.
Cons
- Higher interest rates: Fixed rates are usually higher than variable rates, especially in low-rate environments.
- Less flexibility: If rates drop significantly, you’re locked into your higher rate unless you refinance, which could involve penalties.
- Not ideal for short-term ownership: If you plan to sell within a few years, a fixed-rate mortgage may not provide the best value.
- Potential prepayment penalties: Paying off your mortgage early or breaking your contract could come with fees.
Variable-Rate Mortgages
A variable-rate mortgage in Canada is a home loan where the interest rate changes throughout the term, fluctuating in response to market conditions and the lender’s prime rate. Unlike a fixed-rate mortgage, the interest rate on a variable-rate mortgage can rise or fall depending on factors like the Bank of Canada’s overnight rate, which influences how much interest borrowers will pay over time. This Canadian mortgage type can offer lower rates initially but comes with more unpredictability.
How It Works
With a variable-rate mortgage in Canada, your interest rate is tied to the lender’s prime rate, which moves in step with changes in the market. As a result, your monthly payment may fluctuate, with more or less of your payment going toward interest versus principal. The amount you pay can change even if the term of your mortgage remains the same. While variable rates are generally lower than fixed rates at the beginning, they carry the risk of increasing if the market shifts unfavorably.
Pros
- Potential for lower interest rates: In a low-rate environment, variable mortgages can save you money in interest payments.
- More flexibility: Some lenders allow switching from a variable to a fixed-rate mortgage without penalties.
- Lower break penalties: If you need to break the mortgage early, the penalties are usually lower compared to fixed-rate mortgages.
- Possible short-term savings: Great for those who plan to sell or refinance in a few years before rates could rise.
Cons
- Uncertainty: As market conditions change, so do your payments, which can make long-term financial planning more difficult.
- Higher risk: If interest rates rise, you could end up paying significantly more over time compared to a fixed-rate mortgage.
- Stress from fluctuating payments: For some, the constant possibility of rising rates can create anxiety, especially in a volatile market.
- Potentially higher conversion costs: If you switch to a fixed-rate mortgage when rates are higher, you could lock in at a less favorable rate.
Hybrid Mortgages
A hybrid mortgage is a less common but versatile option that combines elements of both fixed-rate and variable-rate mortgages. This type of mortgage splits the loan into different portions, with one part having a fixed interest rate and the other a variable rate. By doing so, borrowers can benefit from the stability of a fixed rate while also taking advantage of potential savings if variable rates decrease.
This option is best suited for savvy borrowers who want a balanced approach and are comfortable managing the blend of fixed and variable rates in their financial strategy.
Pros
- Flexibility: Combines the stability of fixed rates with the potential savings of variable rates.
- Risk management: Protects you from rising interest rates with the fixed portion, while allowing you to benefit from falling rates with the variable portion.
- Balanced approach: Offers a middle ground for borrowers who want both security and the possibility of savings.
Cons
- Complexity: Each portion may have different terms, making the mortgage harder to manage.
- Transfer difficulty: May be more challenging to switch lenders or refinance due to the mixed structure.
- Less common: Not all lenders offer hybrid mortgages, which could limit your options.
Canadian Mortgage Types: Which is Right for You?
The best choice between fixed, variable, and hybrid mortgages depends entirely on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and how long you plan to own your home.

Fixed-Rate Mortgage: Best for buyers seeking long-term stability and predictable payments
If you’re the type of buyer who values stability and plans to stay in your home for the long haul, a fixed-rate mortgage is a smart choice.
Let’s say you’re a young family purchasing your first home, and you want to ensure your payments stay consistent as you manage other expenses like childcare or schooling. Fixed rates offer peace of mind since your monthly payments won’t change, making it easier to budget over time—even if interest rates rise in the broader market.
Variable-Rate Mortgage: Best for buyers comfortable with risk, looking for potential short-term savings
On the other hand, if you’re comfortable with a little uncertainty and are looking for potential savings, a variable-rate mortgage could be ideal.
Imagine you’re a professional in your early 30s, expecting salary increases or bonuses in the near future. A variable rate might start lower than a fixed rate, offering short-term savings. Plus, if you’re planning to sell or refinance within five years, the lower initial payments can be a significant advantage, especially in a low-rate environment.
Hybrid Mortgage: Best for savvy homebuyers wanting a mix of security and flexibility.
For those who want a bit of both worlds, a hybrid mortgage is perfect. Let’s say you’re a more financially savvy buyer, perhaps someone purchasing a second property or an investment home. You want the security of a fixed rate for a portion of your mortgage but are also willing to gamble on a lower variable rate to potentially save money.
This option gives you the flexibility to balance risk and reward, protecting you from rate spikes while still allowing you to take advantage of market dips.
Conclusion
Choosing the right mortgage type—whether fixed, variable, or hybrid—depends on your financial goals and risk tolerance. By understanding the pros and cons of each option, you’ll be better equipped to make an informed decision.
Looking for the right mortgage solution? With access to over 35 lenders—including banks, credit unions, and private lending companies across Canada—Cruz Financial Group has options for every homebuyer. Let us help you find the mortgage that fits your needs perfectly.





